“Leonardo Innovates: Crafting Robotic Arms for Mars Exploration with NASA and ESA”
Mars robotic exploration stands at the forefront of recent global space endeavors. Leonardo plays a significant role in the examination of pioneering robotic technologies which can aid in unveiling the mysteries of the Red Planet. Under the NASA “Mars Sample Return” initiative, in partnership with the European Space Agency (ESA), Leonardo has secured a contract with Airbus for the advanced study phase (Advanced B2) of the ESA’s Sample Fetch Rover (SFR) robotic arm and has been allocated funding from ESA to advance the research of the Sample Transfer Arm (STA) for the NASA lander.
Thanks to the substantial support from the Italian Space Agency, Leonardo is deeply engaged in the study of two essential components for the 2026 mission of the Mars Sample Return initiative: the arm of the rover and that of the lander. For both elements, Leonardo is dedicated to designing the respective robotic systems for the acquisition and handling of samples.
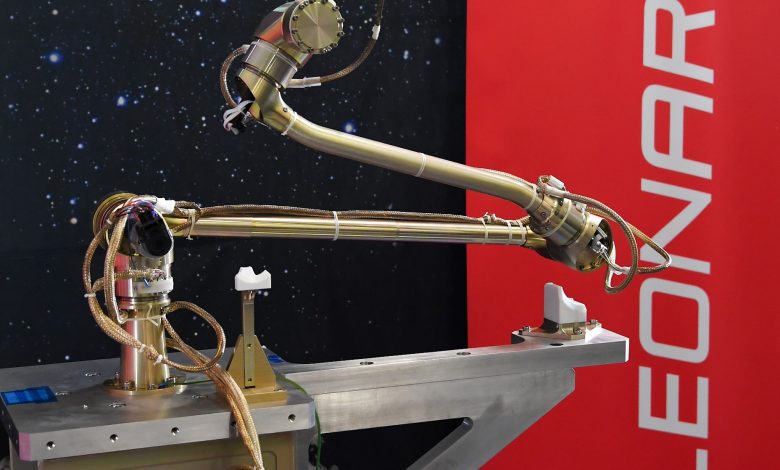
The SFR industrial consortium is spearheaded by Airbus UK. The design of the SFR robotic arm, following an initial phase of conceptual analysis and trials, is now advancing into a more developed phase with the creation of the first prototype (breadboard) to demonstrate the system’s impressive capabilities. The arm can extend up to approximately 110 cm, featuring a control system with 6 degrees of freedom and is fitted with a gripper at its end. The STA of the NASA lander presents a greater complexity, possessing 7 degrees of freedom and extending over 200 cm, with the development phase of the breadboard now underway. Leonardo leads the global industrial consortium responsible for the design of the control electronics, software, and vision system.
The designs of both SFR and STA robotic arms leverage the experiences gained from the development of the Leonardo DELIAN and DEXARM models, which remain regarded as benchmarks in the European space sector. Furthermore, the Company possesses extensive expertise in the space drilling domain, having engineered drills for missions like Rosetta, ExoMars, and Luna-27.
For the MSR initiative, Leonardo will also play a role in the Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) through Thales Alenia Space (a joint venture where Thales holds 67% and Leonardo 33%), responsible for supplying the communication infrastructure enabling data exchange between Earth, ERO, and Mars. This entails designing the essential Orbit Insertion Module and overseeing the Assembly Integration and Test (AIT) phase for the Proto-Flight model of the ERO spacecraft.
Mars Sample Return (MSR)
The collaborative ESA/NASA MSR initiative encompasses three missions aimed at launching from 2020 onwards. These missions will work synergistically to achieve the ambitious objective of retrieving Mars soil samples and returning them to Earth by 2031.
The inaugural NASA mission “Mars2020“, which launched in July, will see the rover Perseverance drill into the Martian terrain and gather samples of the surface material. Perseverance will securely seal the rock and soil samples within specialized tubes and strategically deposit them in locations awaiting collection by subsequent missions.
Targeted for launch in 2026, the “Sample Retrieval Lander” is the second mission of the MSR initiative. This mission comprises three components: the NASA lander, the ESA Sample Fetch Rover, and the Mars Ascent Vehicle (MAV). Leonardo is engaged in studying the arms for both the NASA lander and the ESA rover, each featuring distinct characteristics and responsibilities. Through its robotic arm, the rover will seek out and collect the sample tubes, transferring them to the NASA lander. Subsequently, the NASA lander, utilizing its ESA arm, will position the samples into the MAV, which will launch them in a specialized capsule into Martian orbit.
Finally, the third mission, the “Earth Return Orbiter” (ERO), will be scheduled based on its mission of capturing the capsule in orbit and transporting it back to Earth. Leonardo, in collaboration with Thales Alenia Space, will contribute crucial components of the orbiter. The landing is anticipated in Utah (USA).









